Quiet Start and Particle Loading in PIC Simulations
Project developed in VSim and MATLAB
Overview
This project focuses on implementing a quiet start algorithm for initializing particles in Particle-in-Cell (PIC) simulations. The goal was to reduce numerical noise and better match analytical predictions for instability growth in plasma systems. I developed a MATLAB code to generate initial particle positions and velocities and loaded them into VSim for validation.
Methodology
The particles were distributed in phase space using the cumulative density inversion method. Positions were generated using a bit-reversed sequence, while velocities followed a quiet Maxwellian distribution to minimize noise. This ensured uniform spatial loading and low-discrepancy velocity sampling.
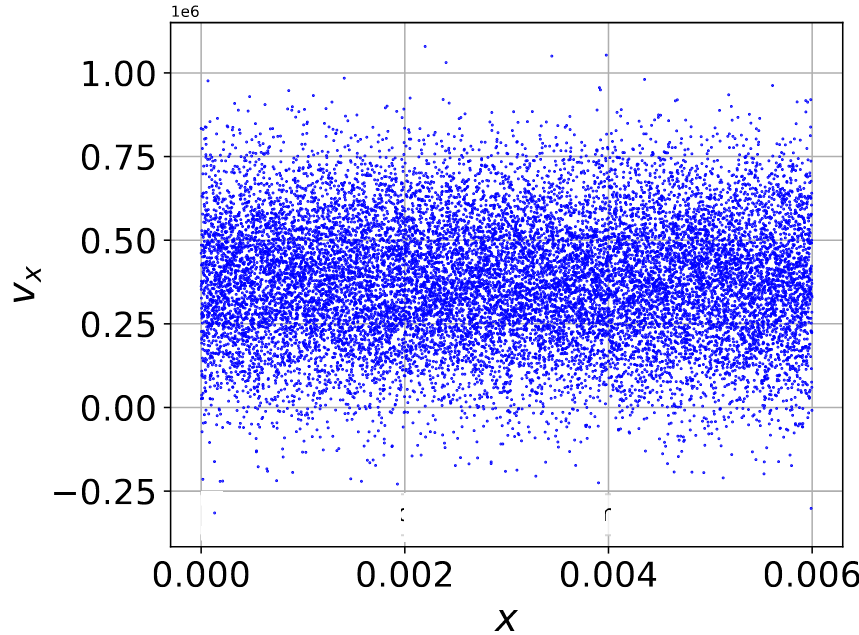
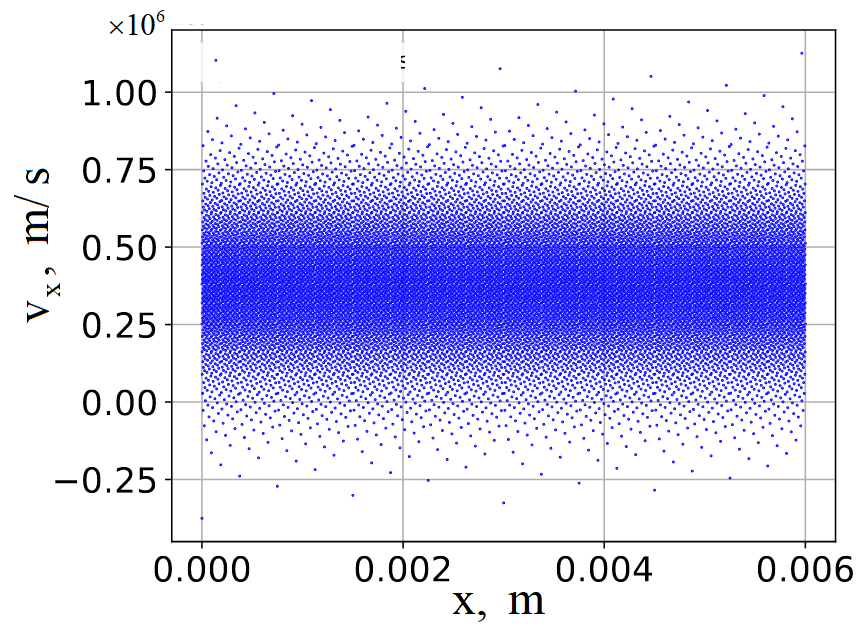
The figure above compares random versus quiet-start velocity initialization, showing the smooth phase-space obtained using the quiet-start scheme.
Results
The quiet start approach drastically reduced the initial electrostatic energy noise (from 10⁹ eV to 10⁵ eV) and delayed instability onset, matching analytical growth rates with less than 1% error in key modes.
| Mode (m) | Analytical Growth Rate (×10⁸ s⁻¹) | Simulation (VSim) |
|---|---|---|
| 30 | 0.90 | 0.82 |
| 37 | 1.08 | 1.11 |
| 44 | 1.17 | 1.14 |
| 51 | 1.07 | 1.16 |
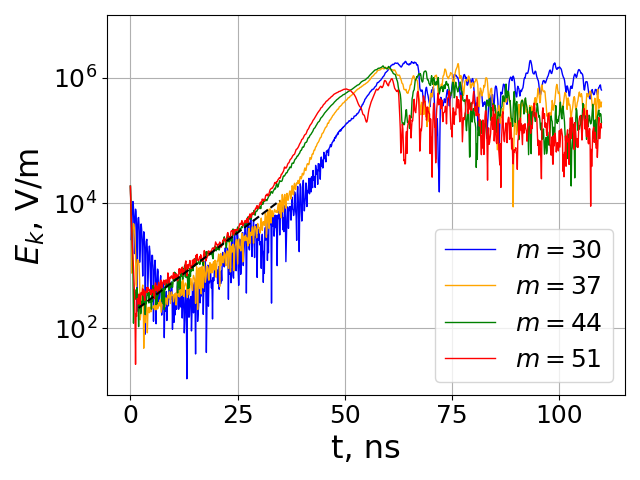
The figure above shows evolution of individual modes of the electric field in quiet start simulation with VSim
Key Contributions
- Developed MATLAB code for quiet-start initialization based on Birdsall’s Xes1 method.
- Implemented quiet-start particle loading into VSim simulations.
- Performed Fourier analysis of electric fields and compared growth rates with analytical models.
- Demonstrated over four orders of magnitude reduction in initial numerical noise.
Conclusion
The quiet-start initialization method provides a stable, low-noise starting point for plasma simulations, ensuring accurate reproduction of linear instability behavior and improved numerical performance in VSim.
← Back to Projects